DocumentationAeminiumRuntime
The main goal of the Æminium Runtime is to paralyze a given code.
Contents
Preparing the ground
To be written...
A Simple Program
Creating the tasks
Every Æminium program should begin by creating an instance of the Runtime class using the proper factory, starting the scheduler by invoking the method init(). It should also terminate with the shutdown(), but we will remind you at the end of the section.
1 public static void main(String[] args)
2 {
3 final Runtime rt = Factory.getRuntime();
4 rt.init();
5
6 Your code goes here!
7
8 rt.shutdown();
9 }
Once you have started the scheduler, it’s time to declare all the tasks and bodies that will turn your program into reality. Every task receives as an argument a body, which it will execute, as well as a constant named HINTS, which will provide useful information to the Runtime, so optimization decisions may occur. It should be also noted the existence of the dataGroup, which allows mutual exclusion between two AtomicTasks. It works like a lock, making sure that two AtomicTasks with the same dataGroup won’t be executing simultaneously.
1 /* First, create a body. */
2 Body b1 = new Body() {
3 public void execute(Runtime rt, Task parent) {
4 int sum = 0;
5 for (int i = 0; i < MAX_CALC; i++) {
6 sum += i;
7 }
8
9 System.out.println("Sum: " + sum);
10 }
11 };
12
13 /* Then, create the task. */
14 Task t1 = rt.createNonBlockingTask(b1, Runtime.NO_HINTS);
Although a task and body are closely related (as you can’t build a task without assigning it a body), you should bear in mind that they don’t necessarily have an exclusive relation. The reason why you have bodies separated from tasks is that two different tasks may be initialized with the same body. This possibility turns out to be really useful, especially when you want to paralyze a common cycle and divide it through several tasks, for example. With the object that represents the task, you may wish to assign dependencies to it. You only need to give its direct dependencies, although you are free to do as you prefer. Giving a small example, you may have three tasks. The third task depends on the second, while this one depends of the first. This means that the third will depend of the second and the first. At the assignment of the dependencies, you can declare both dependencies, but it is sufficient if you only declare its dependency to the second, assuming that you will say that the second depends on the third. When you start a task, the scheduler takes control of it and it’s to it to decide whether give it work right away or leave it waiting. Therefore, the starting method of a task (TODO: see better this) is non-blocking and the rest of the code will be executed immediately.
Life cycle of a task
As has been mentioned in the previous section, a task is allowed to start when you pass it to the scheduler. Then, the scheduler will be responsible for putting the task into work (or better saying, placing it at one of the working queues). One could think that a task would be terminated once it executed all the code present on its body. However, this would mean that the task could be over before all its children were over too, what would bring many problems to the scheduling. Consequently, a task will be considered finished only when it has executed the body and all its children tasks are over too.
Looking into the machinery
Now that we have looked into the aspect of a simple program, it’s now time to see how everything really works. As the code is executed, every task that is considered ready to be scheduled is placed into a graph, where all its dependencies are present. As this graph is being built by the scheduler, the same entity will have the job of detecting the task that have no dependencies and therefore, may start running. When the scheduler finds a task in these conditions, it is placed in one of the waiting queues available. Basically, every processor that can be used by the AEminium program has a corresponding waiting queue, where all the tasks reserved for that processor are pushed into. It’s a job of the scheduler to make a balanced distribution between all the waiting queues, making sure one of the processors isn’t over burden with work while the others are sleeping. Each waiting queue will have a corresponding thread that is looking to the front of the queue and dispatches tasks as they go. If it finds no waiting tasks at its queue, it can pick to one of the options. The first, he follows the technique named ‘work stealing’, where it looks in the other queues for task that aren’t being processed. If this time saving procedure can’t be taken, the thread falls asleep, till a task is scheduled into its queue. It should also be noted the existence of a special queue. While these previous queues receive all the non-blocking and atomic tasks, this single queue will accept all the blocking tasks (i.e. the ones which require I/O interaction).
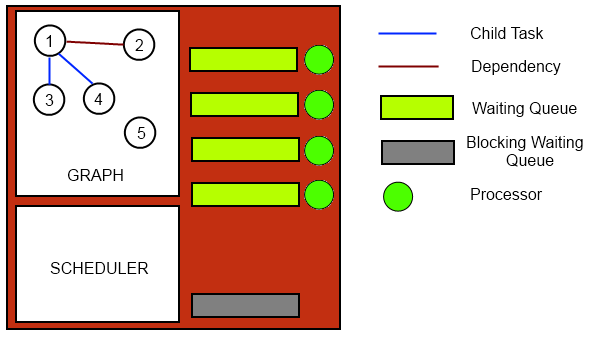
With this, we may define five different states for a task:
- U (Unscheduled)
- WD (Waiting for dependencies)
- R (Running)
- WC (Waiting for Children)
- C (Completed)
Unscheduled is a state that you won’t find that often. A task will be unscheduled if it’s ready to run, but the scheduler hasn’t analyzed it yet. Then, you have the waiting for dependencies state, where a task is blocked due to other task, of which it depends, but haven’t been completed yet. Once all its dependencies are cleaned from the graph (or if the task had no dependencies at the first place) and placed at the waiting queues, a task is marked as running. If a task terminates before all its children are over too, it passes to the waiting for children state. As soon as all this conditions are fulfilled and this task has nothing else to do, the task is marked down as completed. Note however, that even if a task is completed, it isn’t removed from the graph, having instead only all its dependencies vanished. This happens due to consistency problems, as a task that hasn’t been scheduled yet may depend on this very task and if it was cleaned, it would cause a hole in the dependencies list of the new task. When a task reaches this very completed state, it’s its job to remove all the dependencies that point towards it. Also, if by any chance this is a child of another task, it’s also its responsibility to take out itself from its parent’s list where references to all the working children are kept. Finally, if the graph happens to be completely empty (meaning there are no dependencies, with the whole set of nodes being marked as completed) and there are no more tasks to schedule, it means the program has terminated and it now time for the scheduler to call the shutdown(). A promised, we remind you the importance of placing the calling of this method at the end of your program, which will be blocked till the graph is cleaned up.